
A case study on the use of Plone and XML Director as a content management system for the Onkopedia guidelines portal from the German Society of Hematology and Medical Oncology.
The customer
The challenge
The DGHO commissioned Andreas Jung and ZOPYX to extend the guidelines portal in 2014. The aim was for the publication workflow to be automated to the greatest possible extent, since the large volume of documents could no longer be managed by the available manpower. In addition, ZOPYX was to lay the technical groundwork to allow Onkopedia content to be fed directly into external third-party systems (such as hospital information systems) via standardised interfaces. Going forward, this would enable the DGHO to make use of new distribution channels.
The solution
Architecture & technology
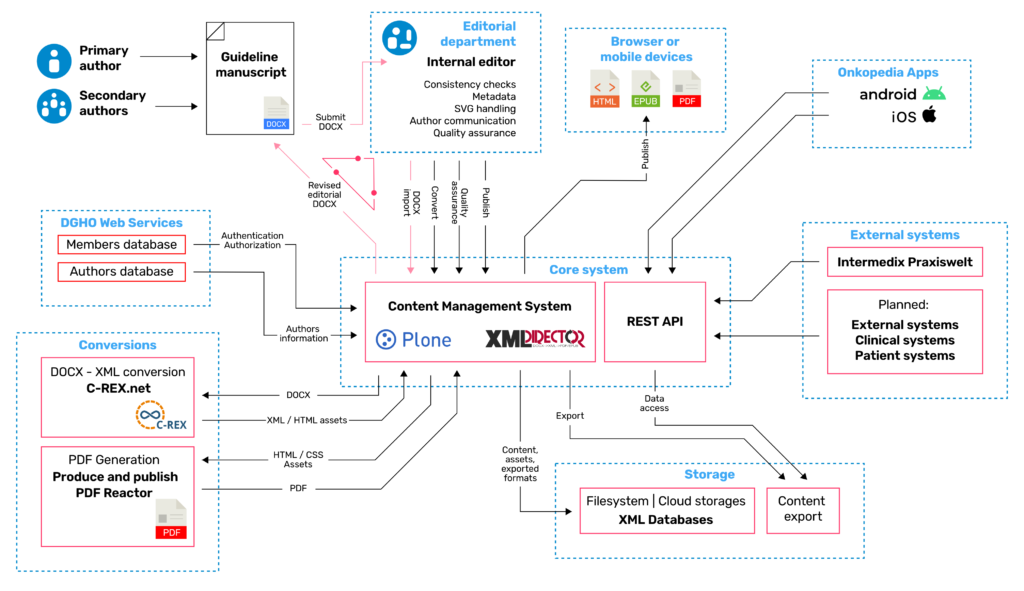
The XML Director extension, which works with Plone 5, was developed by ZOPYX for storing XML content and assets in user-defined storage systems such as file systems, cloud storage or XML databases. Content can be entered through-the-web – via the browser – or imported from DOCX files via open interfaces. XML Director supports external editors like MS Word as well as embedded online editors that run in the browser. All content can be displayed in HTML and made available for download as a PDF or EPUB file. XML Director is an open system and offers powerful CMS functions including role-based access management, adaptable workflows and a simple, intuitive user interface. In addition, as an XML-based system, it is open in all directions and can be networked with standard office software on one side and external systems (via XQuery or WebDAV) on the other. As such, XML Director functions as a central control component in high-grade automated publishing environments.
Onkopedia highlights
DOCX-based processing workflow
XML processing and cross-media storage
- Web/browser: HTML
- Print: PDF
- Apps for smartphones and tablets
- Exports in vendor-specific formats (e.g. for use of content by third parties)
Self-publishing and autonomy over content
Comprehensive, individual master data management
- Document type (guideline, protocol, drug assessments, drug interactions, etc.)
- Storage location (guidelines, drugs, knowledge database, AYApedia, care)
- ICD10 (ICD11 pending)
- ATC codes (for documents related to medicines)
- Participating medical associations
- Date and status
- Authors
- Language
Treatment pathways
Onkopedia app
Four-step publication workflow
- Upload of source data (DOCX documents and treatment pathways)
- Conversion of DOCX to XML
- Conversion to PDF
- Approval and publication
Conflict of interest management
A unified approach for different document types and storage locations
Third-party use of content outside Onkopedia
Automated functions to assist the smooth running of the editorial process
History and facts
- Online since 2010
- Switched to XML in 2014
- Total documents published: 553
- Guidelines, protocols and study results: 325
- Drugs (assessments, factsheets, interactions): 227
- Total documents (incl. archive): ~1800
- Continuous further development and adaptation to technical requirements
- Highly regarded by expert communities in the German-speaking world
Advantages at-a-glance
Reduced workload
The simplified publication workflow with automated quality control significantly reduced the workload of authors and editors. It is only thanks to the combination of simplified operation and extensive automation that such a large number of publications have been able to be handled by a relatively compact team.
Timely publication of changes
Authors and internal editors are able to publish changes to documents promptly and without the involvement of external parties. At the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, this emerged as a ket advantage, since a large amount of COVID-19-related specialist information was required to be published rapidly and updated frequently. The DGHO was able to make the information available quickly and in a targeted manner in a dedicated COVID-19 section.
New distribution options
Third-party systems such as hospital information systems or medical applications can access information directly via open, standardised interfaces.
Effective image-building
Thanks to Onkopedia’s efficient provision of information across multiple channels, the DGHO can confidently position itself as a modern, knowledgeable and highly accomplished medical association.
Greater cost efficiency
The new Onkopedia enabled the DGHO to achieve the highly efficient production of mandatory guidelines and their implementation in clinical practice. The openness of the system renders it excellently placed to adapt to future requirements. Extensions to the scope of services can be realised with minimal time and effort.
Individual solutions are more cost-effective than those off the shelf
All professional associations have different expectations and requirements regarding the publication of guidelines. A standard solution or ‚off-the-shelf‘ software product almost never satisfies all requirements and must often be adapted at great cost. In addition, the purchasing organisation often loses control over its content and is no longer independent (so-called „vendor lock-in“).
The Onkopedia Case Study (old version from 2014) for download:
